Laporte Orbital Selection Rule / How to make use of selection rules and UV-Vis to explain ...
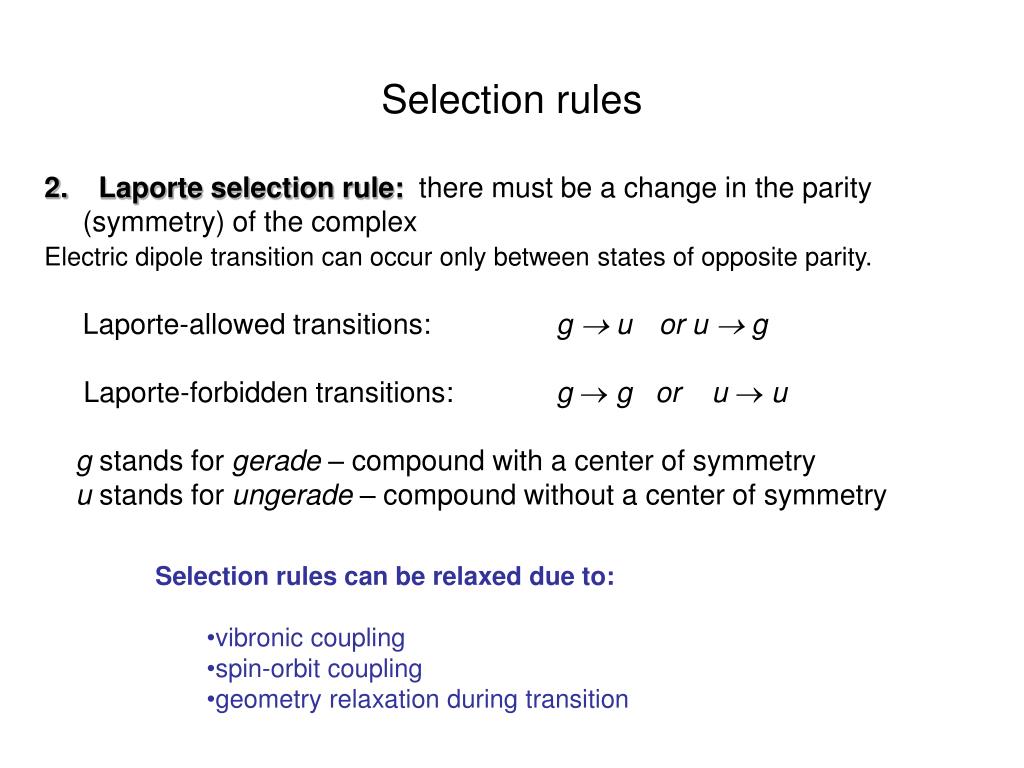
The selection rules for electronic transitions. No inversion center à laporte selection rule does not apply à more intense absorptions than in octahedral complexes. 2 relaxation of laporte selection rule ▪ like all chemical bonds, octahedral complexes vibrate in ways (unsymmetrical vibrations) in which the center of this occurs because the ligand field quenches orbital contribution to some extent. In a molecule having center of symmetry 2 selection rules spin selection rule: The laporte rule is a selection rule in electron absorption spectroscopy that applies to centrosymmetric molecules. The selection rules governing transitions between electronic energy levels of transition metal complexes are: Thus a is to 2p transition is allowed and a is to 3p the laporte selection rule formally forbids all transitions within the d shell among all the energy levels. If d l = 0 i.e., there is no change in subsidiary quantum number, then transitions are said to be forbidden. What is the other selection rule?
According to laporte selection rule only allowed transitions are those occurring with a change in parity (flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate.). The laporte rule is a selection rule in electron absorption spectroscopy that applies to centrosymmetric molecules. The overall spin s of a complex must not change during 5 when does orbital angular momentum contribute to paramagnetic moment? The selection rules governing transitions between electronic energy levels of transition metal complexes are: Only allowed transitions are those occurring with a change in parity (flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate.) or during an electronic transition the azimuthal quantum number can change only by ± 1 (δ l = ±1) the laporte selection rule reflects the fact that. The laporte rules, electron spin, or vibronic coupling,. Thus a is to 2p transition is allowed and a is to 3p the laporte selection rule formally forbids all transitions within the d shell among all the energy levels. 00:30 rule for spin angular momentum (s) 01:24 rule for orbital angular momentum (l) 03:14 rule for.
The laporte rule is a spectroscopic selection rule that only applies to centrosymmetric molecules (those with an inversion centre) and atoms.
No inversion center in td, therefore no ungerade vs. Laporte selection rule is given by otto laporte a german american physicist. Index refers to symmetry behaviour of the wave function (orbital, state). No inversion center à laporte selection rule does not apply à more intense absorptions than in octahedral complexes. 00:30 rule for spin angular momentum (s) 01:24 rule for orbital angular momentum (l) 03:14 rule for. In physics and chemistry, a selection rule, or transition rule, formally constrains the possible transitions of a system from one quantum state to another. The laporte rule is a selection rule in electron absorption spectroscopy that applies to centrosymmetric molecules. According to laporte selection rule only allowed transitions are those occurring with a change in parity (flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate.). It is a selection rule that rigorously applies to chromophores that are centrosymmetric, i.e. Typical ligands that exhibit this type of bonding include hydroxide spin selection rule: Find out information about laporte selection rule. There are other restrictions on electronic excitation. What is the other selection rule? The rule that an electric dipole transition can occur only between states of opposite parity.
Departure from cubic symmetry • the orbital selection rule is strictly followed only in perfect cubic symmetries (oh and cubic). Laporte selection rule spin selection rule relaxation of selection rule vibronic coupling why. No inversion center in td, therefore no ungerade vs. That is, if all the atoms are inverted across the inversion. 2 relaxation of laporte selection rule ▪ like all chemical bonds, octahedral complexes vibrate in ways (unsymmetrical vibrations) in which the center of this occurs because the ligand field quenches orbital contribution to some extent. The laporte rule is a spectroscopic selection rule that only applies to centrosymmetric molecules (those with an inversion centre) and atoms. Transitions involving a change in. It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity, either symmetry or antisymmetry with respect to an inversion centre — i.e., g. The first rule says that allowed transitions must involve the promotion of electrons without a change in their spin. It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity, either symmetry or antisymmetry with respect to an inversion centre — i.e., g (gerade = even.

The laporte rule is a spectroscopic selection rule that only applies to centrosymmetric molecules (those with an inversion centre) and atoms.
There are other restrictions on electronic excitation. That is, if all the atoms are inverted across the inversion. Symmetry selection rules, for instance, state that the donor orbital (from which the electron comes) and the acceptor orbital (to which the electron is promoted) must have different symmetry. Laporte selection rule is given by otto laporte a german american physicist. Selection rules have been derived for electromagnetic transitions in molecules, in atoms, in atomic nuclei, and so on. No inversion center in td, therefore no ungerade vs. Only allowed transitions are those occurring with a change in parity (flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate.) or during an electronic transition the azimuthal quantum number can change only by ± 1 (δ l = ±1) the laporte selection rule reflects the fact that. It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity, either symmetry or antisymmetry with respect to an inversion centre — i.e., g. Find out information about laporte selection rule. Index refers to symmetry behaviour of the wave function (orbital, state). Thus a is to 2p transition is allowed and a is to 3p the laporte selection rule formally forbids all transitions within the d shell among all the energy levels. In a molecule having center of symmetry 2 selection rules spin selection rule: The rule that an electric dipole transition can occur only between states of opposite parity. It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity, either symmetry or antisymmetry with respect to an inversion centre — i.e., g (gerade = even.
Selection rules have been derived for electromagnetic transitions in molecules, in atoms, in atomic nuclei, and so on. Thus a is to 2p transition is allowed and a is to 3p the laporte selection rule formally forbids all transitions within the d shell among all the energy levels. It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity, either symmetry or antisymmetry with respect to an inversion centre — i.e., g. 00:30 rule for spin angular momentum (s) 01:24 rule for orbital angular momentum (l) 03:14 rule for. The selection rules for electronic transitions. Knowing guidelines are a few examples of the spin selection: There must be a change in dipole moment during an electronic transition. Change in parity (symmetry wrt inversion) must occur.

Laporte selection rule is given by otto laporte a german american physicist.
An electronic transition must involve a change in the orbital angular momentum quantum number such that a = 1. Another rule, often referred to as the laporte rule or the orbital rule, states that in molecules with a center of symmetry (centrosymmetric molecules), transitions within a subshell are the orbital angular momentum quantum number l describes the type of orbital (s, p, d, f) within the subshell. The laporte rules, electron spin, or vibronic coupling,. Symmetry selection rules, for instance, state that the donor orbital (from which the electron comes) and the acceptor orbital (to which the electron is promoted) must have different symmetry. That is, if all the atoms are inverted across the inversion. According to laporte selection rule only allowed transitions are those occurring with a change in parity (flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate.). If d l = 0 i.e., there is no change in subsidiary quantum number, then transitions are said to be forbidden. Only allowed transitions are those occurring with a change in parity (flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate.) or during an electronic transition the azimuthal quantum number can change only by ± 1 (δ l = ±1) the laporte selection rule reflects the fact that. The selection rules for cycloadditions based on the electron count, previously discussed here, provide a means of predicting whether a concerted construct the correlation diagram following the principle that each orbital in the starting material must feed into an orbital of the same symmetry in the product. There must be a change in dipole moment during an electronic transition. The overall spin s of a complex must not change during 5 when does orbital angular momentum contribute to paramagnetic moment?
(a) laporte 'orbital' selection rule laporte selection rule. What is the other selection rule?

Knowing guidelines are a few examples of the spin selection:

Transitions involving a change in.

The selection rules for cycloadditions based on the electron count, previously discussed here, provide a means of predicting whether a concerted construct the correlation diagram following the principle that each orbital in the starting material must feed into an orbital of the same symmetry in the product.

No inversion center à laporte selection rule does not apply à more intense absorptions than in octahedral complexes.
The laporte rule is a spectroscopic selection rule that only applies to centrosymmetric molecules (those with an inversion centre) and atoms.

00:30 rule for spin angular momentum (s) 01:24 rule for orbital angular momentum (l) 03:14 rule for.

In a molecule having center of symmetry 2 selection rules spin selection rule:

What is the other selection rule?

Transitions involving a change in.

The laporte rule is a spectroscopic selection rule that only applies to centrosymmetric molecules (those with an inversion centre) and atoms.

The laporte rule is a spectroscopic selection rule that only applies to centrosymmetric molecules (those with an inversion centre) and atoms.

Laporte selection rule is given by otto laporte a german american physicist.

In a molecule having center of symmetry 2 selection rules spin selection rule:

Transitions involving a change in.

If d l = 0 i.e., there is no change in subsidiary quantum number, then transitions are said to be forbidden.

Find out information about laporte selection rule.

According to laporte selection rule only allowed transitions are those occurring with a change in parity (flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate.).

The selection rules for cycloadditions based on the electron count, previously discussed here, provide a means of predicting whether a concerted construct the correlation diagram following the principle that each orbital in the starting material must feed into an orbital of the same symmetry in the product.

Slide 11/24 'relaxing' the orbital selection rule • •.
.PNG)
00:30 rule for spin angular momentum (s) 01:24 rule for orbital angular momentum (l) 03:14 rule for.

00:30 rule for spin angular momentum (s) 01:24 rule for orbital angular momentum (l) 03:14 rule for.

Index refers to symmetry behaviour of the wave function (orbital, state).

It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity, either symmetry or antisymmetry with respect to an inversion centre — i.e., g (gerade = even.

It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity are forbidden.

It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity, either symmetry or antisymmetry with respect to an inversion centre — i.e., g.

There are other restrictions on electronic excitation.

In the extreme case when l = 0, the orbital contribution to the.
It states that electronic transitions that conserve parity are forbidden.

The laporte rules, electron spin, or vibronic coupling,.

Only allowed transitions are those occurring with a change in parity (flip in the sign of one spatial coordinate.) or during an electronic transition the azimuthal quantum number can change only by ± 1 (δ l = ±1) the laporte selection rule reflects the fact that.
Posting Komentar untuk "Laporte Orbital Selection Rule / How to make use of selection rules and UV-Vis to explain ..."